| DXA(デキサ)X線骨密度測定装置 お客様の声 連載・第2部 QUSを用いた骨粗鬆症の診断法 サルコペニアと骨粗鬆症との関連に着目して
|
|||||||||||||
|
骨粗鬆症の診断法、サルコペニアと骨粗鬆症との関連について、 |
| 【地域在住骨粗鬆症患者の運動機能とQOLとサルコペニアとの関連】 |
|
骨粗鬆症の疫学調査においては、運搬可能で簡便無侵襲な超音波骨密度計が適している。筆者の所属する名古屋大学が実施している疫学調査、Yakumo Studyにおける超音波骨密度計を用いた研究を紹介する20。
研究の背景として、骨粗鬆症に関連する障害は高齢者の生活の質(QOL)低下の要因として知られる。一方サルコペニアは移動能力の低下と易転倒性を引き起こすが、骨粗鬆症患者のQOLへの影響は未だに不明であったため、地域在住骨粗鬆症患者においてサルコペニアがQOL低下に与える影響を検討した。
|
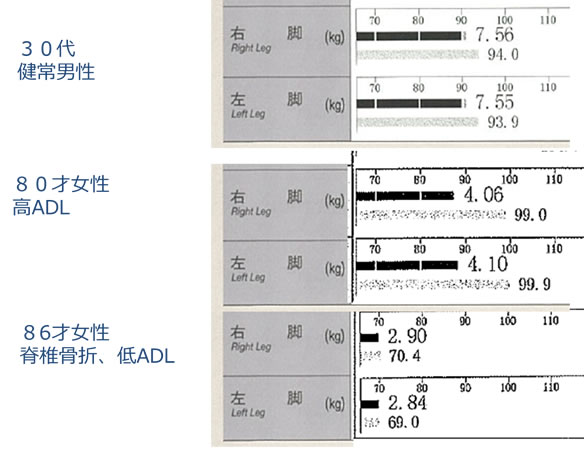
| 【骨粗鬆症患者におけるサルコペニアの診断と筋量評価法】 |
| 【大腿骨頚部骨折・脊椎圧迫骨折とサルコペニア】 |
|
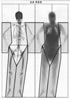
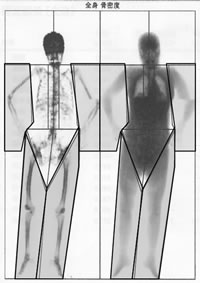
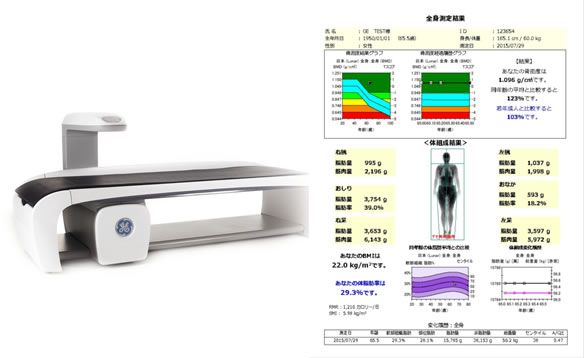
国立長寿医療研究センターにて骨粗鬆症性骨折(大腿骨頚部骨折・脊椎圧迫骨折)を受傷した患者におけるサルコペニアの現状を調査した報告を紹介する31, 32。骨折受傷直後にDXA法により四肢筋量計測を実施し、廃用の影響を排し、より正確に受傷時の筋量を測定した。国立長寿医療研究センターにて入院加療を行った大腿骨近位部骨折患者および椎体骨折患者を対象とし、入院直後にDXA法による筋量測定を行った。骨折のない骨粗鬆症外来通院患者を対照群として一般線形モデルで年齢・性別補正を行い比較した。33
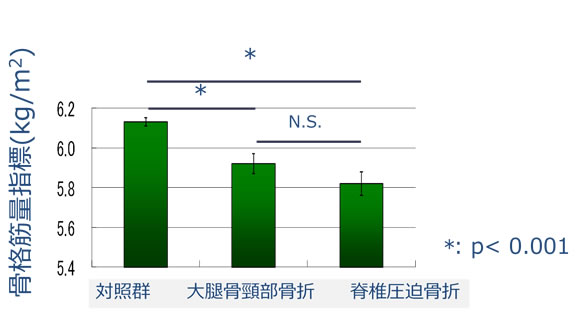
結果、骨格筋量指標(上下肢筋量/身長2)は、対照群が6.13 kg/m2、大腿骨近位部骨折群が5.92kg/m2、椎体骨折群が5.82kg/m2で、骨粗鬆症性骨折患者において有意に筋量の低下が認められた(図11)。
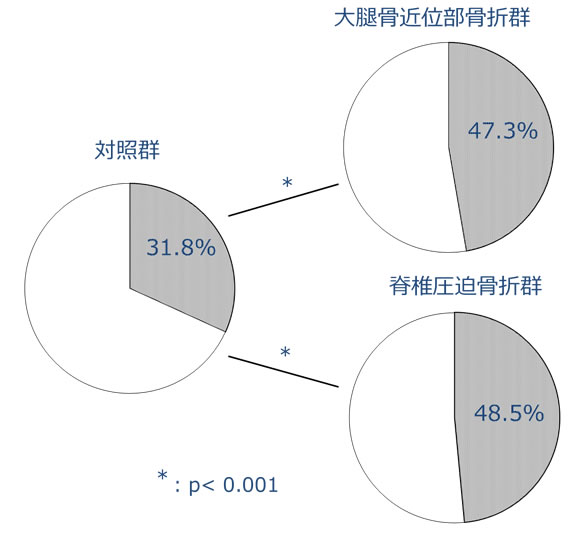
補正四肢筋量の日本人基準値34(女性5.46kg/m2、以下、男性6.87kg/m2以下)をもとに診断したサルコペニアの有病率は、対照群が31.8%、大腿骨近位部骨折群が47.3%、椎体骨折群が48.5%で、骨折患者において有意に有病率が高かった(図12)。骨粗鬆症性骨折患者における深刻なサルコペニア合併の実態が明らかになった。さらに、多変量解析の結果では、大腿骨近位部骨折、椎体骨折はそれぞれサルコペニアが骨密度など他の因子から独立した危険因子であることが判明した。このことから、サルコペニアは骨粗鬆症性骨折の一因であり、骨粗鬆症治療のみならずサルコペニアの治療が骨折予防に重要であることが示唆される。
【引用文献】
20) 飛田哲朗, 今釜史郎, 村本明生, et al. 一般住民の骨粗鬆症患者におけるサルコペニアの実態とQOLへの影響の検討. 日本整形外科学会雑誌 2014; 88: S147. 21) Fielding RA, Vellas B, Evans WJ, et al. Sarcopenia: An Undiagnosed Condition in Older Adults. Current Consensus Definition: Prevalence, Etiology, and Consequences. International Working Group on Sarcopenia. J Am Med Dir Assoc 2011; 12: 249-256. 22) Chen LK, Liu LK, Woo J, et al. Sarcopenia in Asia: consensus report of the Asian Working Group for Sarcopenia. J Am Med Dir Assoc 2014; 15: 95-101. 23) Mazess R, Collick B, Trempe J, Barden H, Hanson J. Performance evaluation of a dual-energy x-ray bone densitometer. Calcif Tissue Int 1989; 44: 228-232. 24) Visser M, Fuerst T, Lang T, Salamone L, Harris TB. Validity of fan-beam dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry for measuring fat-free mass and leg muscle mass. Health, Aging, and Body Composition Study--Dual-Energy X-ray Absorptiometry and Body Composition Working Group. J Appl Physiol 1999; 87: 1513-1520. 25) Wang ZM, Visser M, Ma R, et al. Skeletal muscle mass: evaluation of neutron activation and dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry methods. J Appl Physiol 1996; 80: 824-831. 26) Hoffer EC, Meador CK, Simpson DC. Correlation of whole-body impedance with total body water volume. J Appl Physiol 1969; 27: 531-534. 27) National_Institutes_of_Health. Bioelectrical impedance analysis in body composition measurement: National Institutes of Health Technology Assessment Conference Statement. Am J Clin Nutr 1996; 64: 524S-532S. 28) Tanimoto Y, Watanabe M, Sun W, et al. Association between sarcopenia and higher-level functional capacity in daily living in community-dwelling elderly subjects in Japan. Arch Gerontol Geriatr 2012; 55: e9-e13. 29) Lang T, Cauley JA, Tylavsky F, Bauer D, Cummings S, Harris TB. Computed tomographic measurements of thigh muscle cross-sectional area and attenuation coefficient predict hip fracture: the health, aging, and body composition study. J Bone Miner Res 2010; 25: 513-519. 30) Baumgartner RN, Koehler KM, Gallagher D, et al. Epidemiology of sarcopenia among the elderly in New Mexico. Am J Epidemiol 1998; 147: 755-763. 31) Hida T, Ishiguro N, Sakai Y, Ito K, Harada A. Sarcopenia as a Potential Risk Factor for Osteoporotic Vertebral Compression Fracture in Japanese Elderly Individuals. J Spine Res 2012; 3: 357. 32) Hida T, Ishiguro N, Shimokata H, et al. High prevalence of sarcopenia and reduced leg muscle mass in Japanese patients immediately after a hip fracture. Geriatr Gerontol Int 2012: no-no. 33) Hida T, Ishiguro N, Shimokata H, et al. High prevalence of sarcopenia and reduced leg muscle mass in Japanese patients immediately after a hip fracture. Geriatr Gerontol Int 2013; 13: 413-420. 34) Sanada K, Miyachi M, Tanimoto M, et al. A cross-sectional study of sarcopenia in Japanese men and women: reference values and association with cardiovascular risk factors. Eur J Appl Physiol 2010; 110: 57-65. ※お客様の使用経験に基づく記載です。仕様値として保証するものではありません。 資料請求などのお問い合わせがございましたらこちらまで |